In early March, a spring storm ravaged much of the region served by Logan County Electric Cooperative in Bellefontaine.
“System reliability and safety are extremely important,” says Scott Roach, director of engineering services at LCEC. “With every new project, every work plan, it’s always with that in mind.”
Foliage foibles
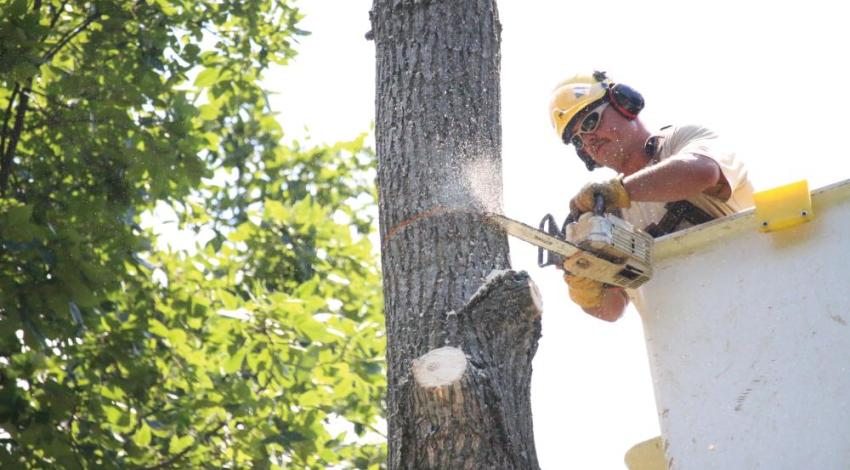
One of the most significant factors affecting that reliability is the presence of trees. Of course, properly placed trees not only are beautiful to look at, but they also provide tangible benefits: increasing property values, reducing the cost to heat and cool a home, providing privacy, and even cutting stormwater runoff.